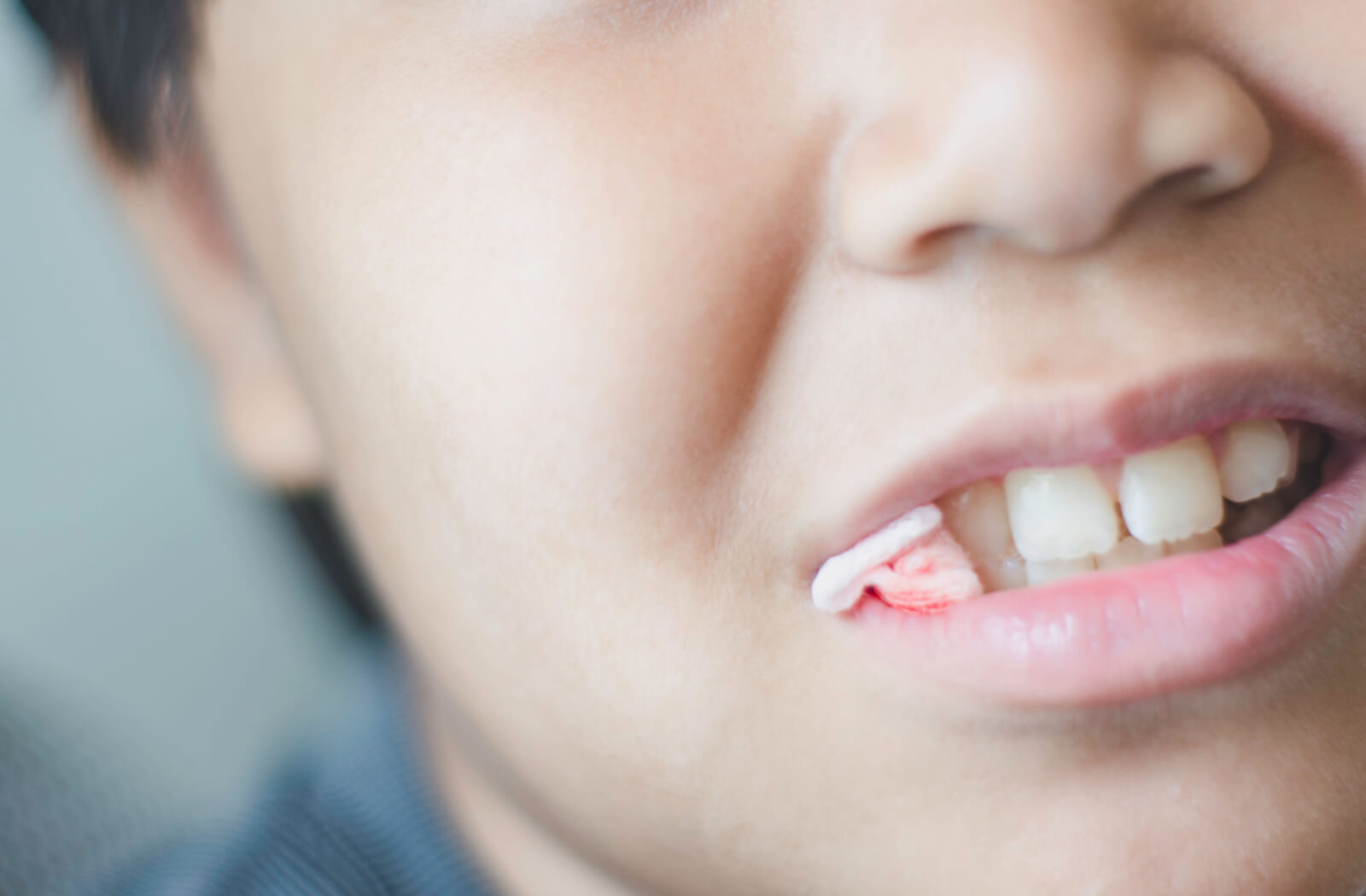
Ultimate Guide To Extraction Gauze: Essential Uses And Benefits
Extraction gauze is an integral part of modern medical practices, playing a crucial role in wound management and surgical procedures. As a versatile and indispensable tool, it provides necessary support for wound healing, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care. With the growing advancements in medical technology, extraction gauze has evolved significantly, offering enhanced features that cater to a wide range of medical needs. This article aims to delve into the various aspects of extraction gauze, providing a comprehensive understanding of its uses, benefits, and significance in healthcare.
In the medical field, precision and reliability are of utmost importance, and extraction gauze meets these demands with its superior design and functionality. With its ability to manage exudate, protect wounds, and minimize the risk of infection, extraction gauze has become a staple in hospitals, clinics, and emergency rooms worldwide. As healthcare professionals continue to prioritize patient safety and comfort, the use of extraction gauze has proven to be a game-changer in enhancing patient outcomes and improving the overall quality of care.
Understanding the nuances of extraction gauze is essential for both medical professionals and patients alike. By exploring its various applications, features, and benefits, individuals can make informed decisions regarding wound care and management. As we navigate through this guide, we will uncover the unique properties of extraction gauze and its impact on the healthcare industry, ensuring that readers gain valuable insights into this critical component of medical treatment.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Extraction Gauze
- The Evolution of Extraction Gauze in Medical Practices
- Key Features and Benefits of Extraction Gauze
- Types of Extraction Gauze: Which One to Choose?
- Applications of Extraction Gauze in Healthcare
- How Extraction Gauze Enhances Wound Healing
- Proper Usage and Techniques for Applying Extraction Gauze
- Common Challenges and Solutions in Using Extraction Gauze
- Innovations and Future Trends in Extraction Gauze
- Comparing Extraction Gauze with Other Wound Care Products
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Extraction Gauze
- Frequently Asked Questions about Extraction Gauze
- Conclusion: The Role of Extraction Gauze in Modern Healthcare
Introduction to Extraction Gauze
Extraction gauze, a fundamental component in wound care, is designed to provide optimal moisture balance, protection, and support for healing wounds. Its soft and absorbent nature makes it suitable for various medical applications, including surgical procedures, first aid, and chronic wound management. By effectively managing exudate and preventing infection, extraction gauze ensures a conducive environment for wound healing, ultimately promoting faster recovery times for patients.
Historically, gauze has been used in medical settings for centuries, with its origins tracing back to the use of natural fibers for dressing wounds. Over time, technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated forms of gauze, including extraction gauze, which offers enhanced functionality and versatility. This evolution highlights the importance of continuous innovation in the medical field, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Extraction gauze is available in various forms, including sterile and non-sterile options, woven and non-woven materials, and differing thicknesses and sizes. This diversity allows healthcare professionals to select the most appropriate type of gauze for each specific wound or medical procedure, ensuring optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction. As we delve deeper into the world of extraction gauze, we will explore its various applications, advantages, and the critical role it plays in modern healthcare.
The Evolution of Extraction Gauze in Medical Practices
The journey of extraction gauze in medical practices is a testament to the ever-evolving nature of healthcare. From its humble beginnings as a simple cotton weave, gauze has transformed into a sophisticated tool that is integral to modern medicine. The development of extraction gauze can be attributed to the ongoing pursuit of improved wound care solutions that enhance patient outcomes and streamline medical procedures.
In the early days of medicine, gauze was primarily made from natural fibers such as cotton and linen, which were woven into simple fabric sheets. These basic forms of gauze provided rudimentary wound coverage, but they lacked the advanced features required for effective wound management. As medical knowledge expanded, the need for more specialized wound care products emerged, leading to the creation of extraction gauze with enhanced absorbency, durability, and sterility.
The 20th century marked a significant turning point in the evolution of extraction gauze, with the introduction of synthetic materials and advanced manufacturing techniques. These innovations allowed for the production of gauze with improved properties, such as increased absorbency, reduced linting, and greater resistance to tearing. The development of sterile gauze further revolutionized wound care, providing a safer option for surgical procedures and reducing the risk of infection.
The advent of non-woven gauze in the latter half of the 20th century offered additional benefits, such as increased softness, flexibility, and adaptability to wound contours. This type of gauze is made from synthetic fibers that are bonded together, creating a highly absorbent and conformable material that is ideal for managing a wide range of wounds. As a result, non-woven extraction gauze has become a popular choice among healthcare professionals, particularly for delicate or sensitive skin.
Today, extraction gauze continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on enhancing its properties and expanding its applications. Innovations such as antimicrobial gauze, advanced wound dressings, and eco-friendly materials are paving the way for the future of wound care, providing new solutions for managing complex medical scenarios. As we explore the various aspects of extraction gauze, it is essential to recognize the significant impact that these advancements have had on the healthcare industry and the lives of patients worldwide.
Key Features and Benefits of Extraction Gauze
Extraction gauze is lauded for its unique features and numerous benefits, making it an essential component of wound care and medical treatments. Understanding these features and benefits allows healthcare professionals to make informed decisions when selecting the most appropriate gauze for specific medical needs.
Absorbency and Exudate Management
One of the primary features of extraction gauze is its exceptional absorbency, which plays a crucial role in managing wound exudate. The gauze's ability to absorb and retain fluids ensures that the wound remains dry and clean, preventing the growth of bacteria and reducing the risk of infection. This feature is particularly beneficial for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate, where effective fluid management is essential for optimal healing.
Softness and Comfort
Extraction gauze is designed to be soft and gentle on the skin, providing a comfortable experience for patients during wound care. This is especially important for individuals with sensitive or fragile skin, as the gauze's non-abrasive texture minimizes irritation and discomfort. The softness of extraction gauze also makes it suitable for use in sensitive areas, such as the face or other delicate regions of the body.
Conformability and Versatility
The versatile design of extraction gauze allows it to conform easily to the contours of the body, ensuring optimal coverage and protection for wounds. This adaptability makes it suitable for use in a wide range of medical applications, from surgical procedures to first aid and chronic wound management. Its versatility also extends to different wound types, including abrasions, lacerations, burns, and surgical incisions.
Breathability and Moisture Control
Extraction gauze is engineered to be breathable, allowing air to circulate freely around the wound. This feature promotes a healthy healing environment by preventing the buildup of moisture and reducing the risk of maceration. By maintaining an ideal moisture balance, extraction gauze supports the body's natural healing processes and accelerates wound closure.
Antimicrobial Properties
Many modern extraction gauzes are infused with antimicrobial agents that provide an added layer of protection against infection. These agents work by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and other pathogens, reducing the likelihood of complications and promoting faster healing. Antimicrobial gauze is particularly beneficial for individuals with compromised immune systems or those at higher risk of infection.
In summary, the key features and benefits of extraction gauze make it a valuable tool in medical practices. Its absorbency, softness, conformability, and antimicrobial properties contribute to effective wound management and improved patient outcomes. As we continue to explore the various aspects of extraction gauze, it is clear that its role in healthcare is indispensable, providing essential support for wound healing and overall patient care.
Types of Extraction Gauze: Which One to Choose?
Understanding the variety of extraction gauze types available is crucial for selecting the most suitable option for specific medical needs. Each type of gauze offers distinct advantages, making it important to consider factors such as wound type, exudate level, and patient comfort when making a choice.
Woven Extraction Gauze
Woven extraction gauze is made from cotton fibers woven into a tight mesh, providing excellent absorbency and strength. This type of gauze is ideal for heavy exudate wounds, as its dense structure allows for effective fluid management. Woven gauze is also highly durable, making it suitable for use in surgical procedures where stability and reliability are essential.
Non-Woven Extraction Gauze
Non-woven extraction gauze is created by bonding synthetic fibers together, resulting in a soft, flexible, and highly absorbent material. This type of gauze is favored for its gentle texture, making it suitable for sensitive or fragile skin. Non-woven gauze is also less likely to shed fibers, reducing the risk of leaving lint in the wound and minimizing irritation.
Antimicrobial Extraction Gauze
Antimicrobial extraction gauze is infused with agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria and other pathogens, providing enhanced protection against infection. This type of gauze is particularly beneficial for wounds with a high risk of infection, such as surgical incisions or chronic wounds. The antimicrobial properties help reduce complications and promote faster healing, offering peace of mind for both patients and healthcare providers.
Impregnated Extraction Gauze
Impregnated extraction gauze is coated with substances such as petroleum, iodine, or silver, which provide additional therapeutic benefits. These substances can offer antimicrobial protection, promote moisture retention, or assist in debriding the wound, depending on the specific needs of the patient. Impregnated gauze is often used for complex or non-healing wounds, where additional support is required to facilitate healing.
Sterile vs. Non-Sterile Gauze
Extraction gauze is available in both sterile and non-sterile options, with each serving different purposes. Sterile gauze is used in surgical procedures and for dressing open wounds, where maintaining a sterile environment is critical to prevent infection. Non-sterile gauze, on the other hand, is suitable for cleaning and covering closed wounds or for use in first aid applications where sterility is not a primary concern.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate type of extraction gauze depends on several factors, including the wound type, exudate level, and individual patient needs. By understanding the distinct characteristics of each type, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that enhance patient care and support optimal healing outcomes.
Applications of Extraction Gauze in Healthcare
Extraction gauze serves a multitude of purposes in healthcare settings, providing essential support for a wide range of medical applications. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals across various specialties, from emergency medicine to chronic wound management.
Surgical Procedures
In surgical settings, extraction gauze is commonly used to manage bleeding, absorb exudate, and protect incisions. Its high absorbency and durability make it ideal for use during and after surgical procedures, ensuring that the surgical site remains clean and dry. Additionally, sterile extraction gauze is utilized to maintain a sterile environment, reducing the risk of postoperative infections and complications.
Wound Care and Management
Extraction gauze is a staple in wound care, providing essential support for managing various wound types, including cuts, abrasions, lacerations, and burns. Its ability to absorb fluids and protect wounds from contaminants makes it an effective dressing option, promoting an optimal healing environment. Extraction gauze is also used to cover and protect chronic wounds, such as pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers, where long-term management is required.
First Aid and Emergency Care
In first aid and emergency care scenarios, extraction gauze is a vital component of wound management kits. Its portability and ease of use make it ideal for quickly addressing injuries in the field, providing immediate protection and support for wounds until further medical attention can be obtained. Extraction gauze is also used to control bleeding and stabilize injured areas, ensuring that patients receive prompt and effective care in emergency situations.
Burn Treatment
Extraction gauze plays a critical role in burn treatment, where its soft and non-abrasive texture offers comfort and protection for delicate skin. Its absorbency helps manage exudate from burn wounds, while its breathability promotes a healthy healing environment. In cases of severe burns, specialized extraction gauze impregnated with therapeutic agents may be used to support healing and reduce the risk of infection.
Dental Procedures
In dental procedures, extraction gauze is used to manage bleeding and absorb fluids during tooth extractions and other oral surgeries. Its compact size and high absorbency make it suitable for use in the oral cavity, providing effective support for post-operative care. Dental professionals rely on extraction gauze to ensure that patients experience minimal discomfort and optimal healing following dental procedures.
Overall, the diverse applications of extraction gauze in healthcare highlight its importance as a versatile and reliable tool for medical professionals. Its ability to adapt to various medical scenarios and support effective wound management underscores its value in promoting positive patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of care.
How Extraction Gauze Enhances Wound Healing
The role of extraction gauze in wound healing is multifaceted, with its unique properties contributing to a conducive environment for the body's natural healing processes. By understanding how extraction gauze supports wound healing, healthcare professionals can optimize their wound care practices and improve patient outcomes.
Moisture Balance and Exudate Management
Extraction gauze plays a crucial role in maintaining the ideal moisture balance for wound healing. Its absorbent properties allow it to effectively manage exudate, preventing the buildup of excess moisture that can lead to maceration and delayed healing. By keeping the wound dry and clean, extraction gauze promotes a healthy healing environment, supporting faster and more efficient tissue repair.
Protection Against Infection
The use of extraction gauze helps protect wounds from external contaminants, reducing the risk of infection. Its barrier function prevents the entry of bacteria and other pathogens, safeguarding the wound and promoting optimal healing conditions. For wounds at higher risk of infection, antimicrobial extraction gauze offers additional protection by actively inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms.
Support for Granulation and Epithelialization
Extraction gauze provides essential support for the processes of granulation and epithelialization, which are key stages of wound healing. By maintaining a stable environment and preventing mechanical disturbance, the gauze allows new tissue to form and epithelial cells to migrate across the wound surface. This support is crucial for achieving complete wound closure and restoring the integrity of the skin.
Reduction of Pain and Discomfort
The soft and non-abrasive texture of extraction gauze minimizes irritation and discomfort for patients, making it suitable for use on sensitive or painful wounds. Its gentle nature reduces the likelihood of trauma during dressing changes, ensuring that the wound remains undisturbed and promoting a more comfortable healing experience for patients.
Facilitation of Autolytic Debridement
Extraction gauze can aid in the process of autolytic debridement, where the body's natural enzymes break down and remove necrotic tissue. By maintaining a moist wound environment, the gauze promotes the activity of these enzymes, facilitating the removal of dead tissue and supporting the growth of healthy tissue. This process is essential for preventing infection and promoting efficient wound healing.
In conclusion, extraction gauze enhances wound healing by providing essential support for moisture balance, infection prevention, and tissue repair. Its role in maintaining a stable and conducive healing environment underscores its value as a critical component of wound care, benefiting both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Proper Usage and Techniques for Applying Extraction Gauze
To maximize the benefits of extraction gauze, it is essential to use proper techniques when applying and changing dressings. Adhering to best practices ensures that the gauze functions effectively, promoting optimal wound healing and minimizing the risk of complications.
Preparation and Hygiene
Before applying extraction gauze, it is crucial to clean the wound area thoroughly to remove any debris, exudate, or contaminants. This step reduces the risk of infection and ensures that the gauze adheres properly to the wound bed. Healthcare professionals should also practice proper hand hygiene and wear gloves to prevent the transfer of bacteria during the dressing application.
Selection of Appropriate Gauze Type
Selecting the right type of extraction gauze is critical for effective wound management. Consider factors such as wound size, exudate level, and patient sensitivity when choosing between woven, non-woven, or antimicrobial gauze. For wounds requiring additional therapeutic support, impregnated gauze may be appropriate.
Application Technique
When applying extraction gauze, ensure that it covers the entire wound surface and extends slightly beyond the wound edges. This coverage provides adequate protection and prevents external contaminants from reaching the wound. Secure the gauze in place using medical tape or a bandage, ensuring that it is snug but not too tight to avoid restricting blood flow.
Regular Dressing Changes
Regularly changing extraction gauze is essential for maintaining a clean and healthy wound environment. The frequency of dressing changes depends on the level of exudate, the wound type, and the gauze's absorbency. Typically, dressings should be changed daily or as needed when saturated with exudate. During dressing changes, assess the wound for signs of infection or complications, and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
Pain Management and Patient Comfort
To minimize discomfort during dressing changes, consider using a non-stick gauze or applying a thin layer of medical ointment to prevent the gauze from adhering to the wound. Encourage patients to communicate any pain or discomfort they experience during the dressing process, and adjust techniques as needed to ensure their comfort and well-being.
In summary, proper usage and techniques for applying extraction gauze are vital for promoting effective wound healing and minimizing the risk of complications. By adhering to best practices and maintaining a patient-centered approach, healthcare professionals can optimize their wound care practices and support positive patient outcomes.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Using Extraction Gauze
While extraction gauze is an invaluable tool in wound care, healthcare professionals may encounter certain challenges when using it. Identifying these challenges and implementing effective solutions can enhance the overall wound management process and improve patient outcomes.
Adhesion to Wounds
One common challenge is the adhesion of extraction gauze to the wound surface, which can cause discomfort and disrupt healing during dressing changes. To address this issue, consider using a non-stick gauze or applying a thin layer of medical ointment to the wound before gauze application. This approach reduces the likelihood of adhesion and minimizes trauma during dressing changes.
Excessive Exudate Management
For wounds with heavy exudate, standard gauze may become saturated quickly, necessitating frequent dressing changes. To manage excessive exudate effectively, consider using a high-absorbency gauze or combining gauze with an absorbent secondary dressing. This solution helps maintain a dry wound environment and reduces the frequency of dressing changes, improving patient comfort and compliance.
Risk of Infection
Infection is a significant concern in wound care, and using the wrong type of gauze can increase this risk. To mitigate infection risks, ensure that the gauze is sterile and appropriate for the wound type. For wounds at high risk of infection, antimicrobial gauze can provide additional protection and reduce complications.
Patient Sensitivity and Allergies
Some patients may experience sensitivity or allergic reactions to certain materials used in extraction gauze. To address this challenge, select hypoallergenic gauze options that are free from latex and other common allergens. Conduct a patch test if necessary to identify any adverse reactions before applying the gauze to the wound.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of medical waste, including used gauze, is a growing concern. To minimize waste, consider using eco-friendly gauze options made from sustainable materials. Encourage responsible disposal practices and explore opportunities for recycling or reusing medical materials where possible.
By recognizing and addressing common challenges in using extraction gauze, healthcare professionals can enhance their wound care practices and support optimal patient outcomes. Implementing effective solutions ensures that extraction gauze functions as intended, promoting efficient healing and maintaining patient comfort and satisfaction.
Innovations and Future Trends in Extraction Gauze
The field of wound care is constantly evolving, with ongoing innovations in extraction gauze playing a pivotal role in advancing medical practices. As technology and research continue to drive progress, several emerging trends are shaping the future of extraction gauze, offering exciting possibilities for improved wound management.
Smart Gauze Technology
Smart gauze technology is an emerging trend that integrates sensors and digital tools into traditional gauze to monitor wound healing in real-time. These sensors can track parameters such as moisture levels, temperature, and pH, providing valuable data for healthcare professionals to assess the wound's condition and progress. Smart gauze has the potential to revolutionize wound care by enabling more personalized and responsive treatment plans.
Advanced Antimicrobial Gauze
Research into advanced antimicrobial agents is leading to the development of new gauze materials with enhanced infection-fighting properties. These agents are designed to target a broader spectrum of pathogens or provide longer-lasting protection, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster healing. Advanced antimicrobial gauze is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic wounds or compromised immune systems.
Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Gauze
The growing emphasis on sustainability is driving the development of biodegradable and eco-friendly gauze options. These products are made from renewable materials that break down naturally, reducing their environmental impact. As healthcare systems strive to minimize waste and promote environmentally responsible practices, biodegradable gauze offers a promising solution for sustainable wound care.
Customizable Gauze Solutions
Advancements in manufacturing techniques are enabling the production of customizable gauze solutions tailored to specific wound types and patient needs. Customizable gauze can be designed to fit unique wound shapes or incorporate specific therapeutic agents, providing more targeted and effective care. This trend aligns with the broader movement toward personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual patients for optimal outcomes.
Integration of Natural Healing Agents
There is increasing interest in the integration of natural healing agents, such as honey, aloe vera, and essential oils, into extraction gauze. These agents offer additional therapeutic benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, enhancing the gauze's ability to support wound healing. The use of natural agents aligns with the growing demand for holistic and alternative approaches to healthcare.
In summary, innovations and future trends in extraction gauze are shaping the landscape of wound care, offering new possibilities for improved patient outcomes and more sustainable practices. As these trends continue to evolve, they hold the potential to transform wound management, providing healthcare professionals with advanced tools to deliver high-quality care and support optimal healing.
Comparing Extraction Gauze with Other Wound Care Products
In the realm of wound care, extraction gauze is one of many products available to healthcare professionals. Comparing extraction gauze with other wound care options can help determine the most appropriate choice for specific medical needs, ensuring optimal patient outcomes and effective wound management.
Extraction Gauze vs. Foam Dressings
Foam dressings are known for their high absorbency and cushioning effect, making them suitable for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate. While extraction gauze is also absorbent, foam dressings offer superior moisture retention and comfort, making them ideal for pressure ulcers and other painful wounds. However, extraction gauze provides greater flexibility and adaptability, making it suitable for a broader range of wound types and applications.
Extraction Gauze vs. Hydrocolloid Dressings
Hydrocolloid dressings are designed to maintain a moist wound environment, promoting autolytic debridement and faster healing. These dressings are ideal for superficial wounds with low to moderate exudate, such as minor burns and abrasions. In contrast, extraction gauze is more versatile and can be used for wounds with varying exudate levels. While hydrocolloid dressings offer convenience and prolonged wear time, extraction gauze provides greater breathability and ease of application.
Extraction Gauze vs. Alginate Dressings
Alginate dressings are derived from seaweed and are highly absorbent, making them suitable for wounds with heavy exudate. These dressings form a gel-like substance upon contact with wound fluid, providing a moist healing environment. Extraction gauze, while absorbent, does not offer the same gel-forming properties as alginate dressings. However, it is more versatile and can be combined with other dressings to enhance its absorbency and functionality.
Extraction Gauze vs. Transparent Film Dressings
Transparent film dressings are thin, adhesive sheets that provide a barrier against bacteria and contaminants while allowing oxygen exchange. These dressings are ideal for superficial wounds with minimal exudate, such as surgical incisions and donor sites. Extraction gauze, on the other hand, offers greater absorbency and is suitable for wounds with varying exudate levels. While transparent film dressings provide visibility and protection, extraction gauze offers more comprehensive wound coverage and management.
Extraction Gauze vs. Hydrogel Dressings
Hydrogel dressings are designed to provide moisture to dry wounds, promoting autolytic debridement and pain relief. These dressings are ideal for dry or necrotic wounds, such as pressure ulcers and burns. Extraction gauze, in contrast, is more versatile and can be used for wounds with varying moisture levels. While hydrogel dressings offer targeted moisture delivery, extraction gauze provides greater flexibility and adaptability for a wide range of wound types.
In conclusion, comparing extraction gauze with other wound care products highlights its versatility and adaptability in managing a wide variety of wounds. While each wound care product offers distinct advantages, extraction gauze remains a valuable tool in medical practice, providing essential support for wound healing and effective patient care.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Extraction Gauze
The environmental impact and sustainability of medical products, including extraction gauze, are becoming increasingly important considerations for healthcare systems worldwide. As the demand for eco-friendly and sustainable practices grows, understanding the environmental implications of extraction gauze and exploring ways to minimize its impact are crucial.
Materials and Manufacturing
The production of extraction gauze involves the use of natural and synthetic fibers, each with its environmental considerations. Cotton, a common material in woven gauze, requires significant water and pesticide use in its cultivation, contributing to environmental degradation. Synthetic fibers, while offering durability and flexibility, are derived from petrochemicals, which have their own environmental footprint. Efforts to source sustainable materials and improve manufacturing processes are essential for reducing the environmental impact of extraction gauze.
Waste Management and Disposal
Medical waste, including used gauze, poses a significant challenge for healthcare facilities. Proper disposal is crucial to prevent contamination and environmental harm. Many healthcare systems are implementing waste management strategies that prioritize recycling and responsible disposal of medical products. Exploring biodegradable or compostable gauze options can also help reduce the environmental impact of waste generated from wound care.
Sustainable Packaging
Sustainable packaging is an important aspect of minimizing the environmental impact of extraction gauze. Reducing the use of plastic packaging and opting for recyclable or biodegradable materials can significantly decrease the carbon footprint associated with medical products. Healthcare systems are encouraged to seek suppliers that prioritize sustainable packaging solutions and adopt eco-friendly practices.
Eco-Friendly Alternatives
As the demand for sustainable healthcare solutions grows, the development of eco-friendly gauze alternatives is gaining traction. These alternatives may include gauze made from renewable resources, such as bamboo or hemp, which require less water and pesticides for cultivation. Additionally, innovations in biodegradable gauze materials offer promising solutions for reducing the environmental impact of wound care products.
Promoting Sustainable Practices
Healthcare facilities play a critical role in promoting sustainable practices and reducing their environmental impact. Implementing eco-friendly policies, such as reducing waste, conserving resources, and prioritizing sustainable products, can contribute to a more sustainable healthcare system. Educating healthcare professionals and patients about the importance of sustainability in wound care is also essential for driving positive change.
In summary, addressing the environmental impact and sustainability of extraction gauze is crucial for fostering a more sustainable healthcare system. By prioritizing eco-friendly materials, waste management practices, and sustainable alternatives, healthcare facilities can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier planet.
Frequently Asked Questions about Extraction Gauze
1. What is extraction gauze used for?
Extraction gauze is primarily used for wound care and management, providing essential support for wound healing by absorbing exudate, protecting against infection, and promoting a conducive healing environment. It is commonly used in surgical procedures, first aid, burn treatment, and dental procedures.
2. How do I choose the right type of extraction gauze?
Choosing the right type of extraction gauze depends on factors such as wound type, exudate level, and patient sensitivity. Consider options such as woven or non-woven gauze for different absorbency needs, and opt for antimicrobial or impregnated gauze for additional therapeutic support.
3. How often should extraction gauze be changed?
The frequency of dressing changes depends on the level of exudate, the wound type, and the gauze's absorbency. Generally, dressings should be changed daily or as needed when saturated with exudate. Regularly changing gauze helps maintain a clean wound environment and supports optimal healing.
4. Can extraction gauze be used for all types of wounds?
Extraction gauze is versatile and can be used for a wide range of wound types, including cuts, abrasions, lacerations, burns, and surgical incisions. However, for wounds with specific needs, such as heavy exudate or dry necrotic tissue, alternative wound care products may be more suitable.
5. What are the benefits of antimicrobial extraction gauze?
Antimicrobial extraction gauze provides enhanced protection against infection by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and other pathogens. It is particularly beneficial for wounds at high risk of infection, such as surgical incisions or chronic wounds, reducing complications and promoting faster healing.
6. Are there eco-friendly options for extraction gauze?
Yes, there are eco-friendly options for extraction gauze, including biodegradable gauze made from renewable resources such as bamboo or hemp. These options offer a more sustainable solution for wound care and help reduce the environmental impact of medical waste.
Conclusion: The Role of Extraction Gauze in Modern Healthcare
Extraction gauze is an indispensable tool in modern healthcare, providing essential support for wound healing and effective patient care. Its versatility, absorbency, and protective properties make it a valuable asset for healthcare professionals across various medical applications, from surgical procedures to chronic wound management.
As the field of wound care continues to evolve, ongoing innovations and research are shaping the future of extraction gauze, offering exciting possibilities for improved patient outcomes and more sustainable practices. By understanding the unique features and benefits of extraction gauze, healthcare professionals can optimize their wound care practices, ensuring that patients receive the highest quality of care.
Ultimately, extraction gauze plays a critical role in promoting positive patient outcomes, enhancing the overall quality of care, and supporting the body's natural healing processes. As we look to the future, the continued advancement and adoption of extraction gauze will undoubtedly contribute to a healthier and more sustainable healthcare system, benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Article Recommendations